ESA chooses GMV as 1 of 3 contractors for new phase of Galileo ground station

The Galileo Second Generation will phase in of new services, improve existing services and increase security
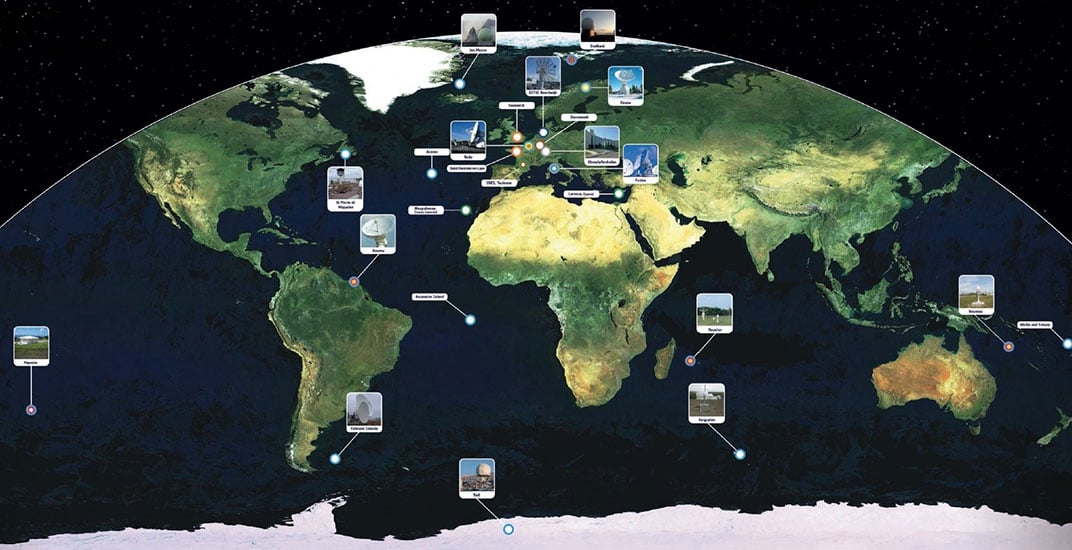
The technology multinational GMV is playing a key role in the Galileo Second Generation (G2G) ground segment.
G2G’s main objectives are to phase in new services, improve existing services, and boost system robustness and security while cutting both operating and maintenance costs, to cement Galileo’s position as one the future’s top GNSS.
Three phases. G2G is divided into several phases. In the first, led by the European Space Agency (ESA), mission requirements were defined at system level. This was followed by a preparation phase, then an implementation phase.
As well as priming several mission-requirement projects, GMV, since 2018, has been heading one of the consortia working on G2G’s complete ground segment during the preparation phase.
Within the preparation phase — shortly before the start of the COVID lockdown — ESA announced the successful end of the first phase before launching a bid invitation for the second phase as the prelude to G2G implementation.
Although publication of the bid invitation for this phase was eventually pushed back until mid-June, GMV never broke off its G2G activities. In recent months GMV has brought new recruitments and partners into the project team while also working on new ideas and kicking off some project activities.
Team members have attended various skills-training courses, some of them gaining certification under SAFe 5 Agilist. During these months, GMV has also been working under new pandemic circumstances with teleworking, virtual meetings and new toolboxes.
First Generation. Galileo First Generation (G1G), running since December 2016, consists of space infrastructure (26 satellites to date) and ground infrastructure. Galileo is now providing 20-cm-precision positioning, navigation and timing services for over 400 million users around the world.















Follow Us