Satelles and NIST team up on precision timing
Cooperative agreement expands precision timing distribution options for critical infrastructure and verifies STL’s agreement with UTC via UTC(NIST)
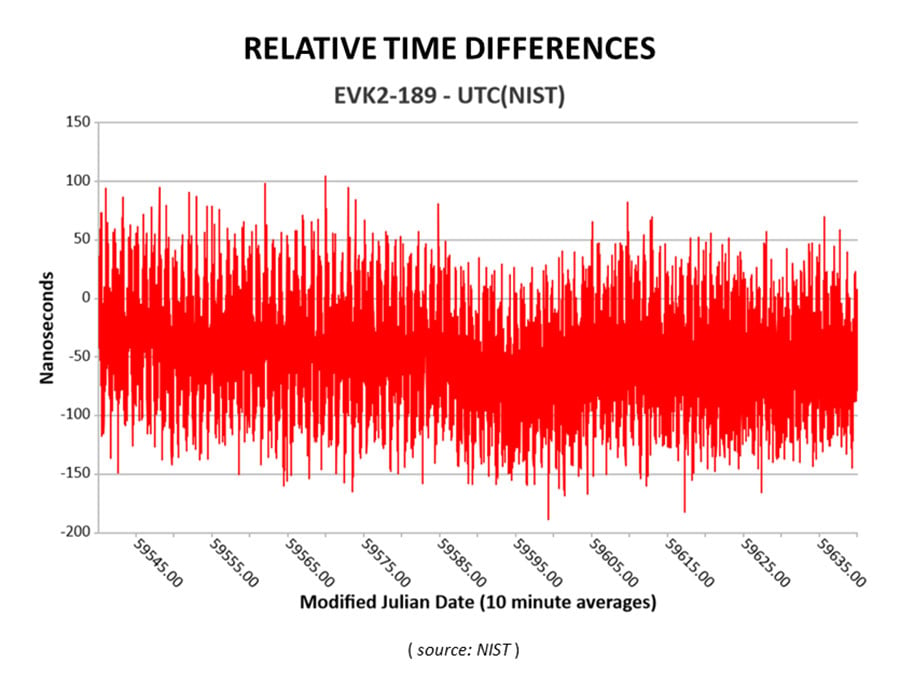
This March 30, 2022, chart of Satelles and NIST testing verifies that STL timing agrees with UTC. (Chart: Satelles)
Satelles Inc., provider of highly secure satellite-based time and location services, has entered a cooperative agreement with the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology that directly connects STL’s operational infrastructure to the source of UTC(NIST), the national standard for time and frequency in the United States produced in coordination with the U.S. Naval Observatory.
The agreement calls for Satelles to provide its STL service to NIST. Reciprocally, the agreement includes the introduction of a connection between an STL Ground Monitoring Station (GMS) provided by Satelles to the NIST collection of extremely accurate atomic clocks that maintains the official time scale for UTC(NIST).
The Cooperative Agreement was described in NIST Technical Note 2187, “A Resilient Architecture for the Realization and Distribution of Coordinated Universal Time to Critical Infrastructure Systems in the United States,” published in November 2021.
In February 2021, Satelles delivered and configured an STL GMS at NIST’s Time and Frequency Division in Boulder, Colorado. This facility is home to the ensemble of high-precision cesium beam and hydrogen maser atomic clocks that maintains UTC(NIST).
After conducting a series of successful preliminary tests in the spring of 2021, NIST then directly connected the STL GMS to its primary clock ensemble in June 2021. Comparing timing provided by STL to UTC(NIST), the testing confirmed STL’s long-term stability of better than 25 nanoseconds with short-term time deviation of 50 nanoseconds.
STL from Satelles is a resilient, alternative PNT service from low-Earth-orbit (LEO) satellites that enterprise customers rely on as a primary timing source. Telecom operators, for example, use STL for 5G wireless network deployments where GPS is unavailable indoors or when other timing solutions cannot provide the required level of accuracy.
STL’s agreement with UTC also is important for critical infrastructure and other applications that require an essential contingency capability to protect the operations of PNT-dependent systems and ensure survivability and resilience.
“Satelles has a network of GMS nodes positioned around the world to receive STL signals and calculate the position and timing of the satellites for purposes of producing timing corrections, and
now we are fortunate to have a GMS connected inside NIST’s main time lab,” said Gregory Gutt, president and CTO of Satelles. “It’s an honor to be given direct access to UTC(NIST), especially in an arrangement that delivers benefit to both our customers and NIST.”
Visit satelles.com/nist for more information about NIST reports that detail the performance of STL and collaborations between Satelles and NIST.
















Follow Us